Camera Type
The camera is crucial as it dictates your viewpoint of the scene. It’s comprises two key elements in the 3D landscape – the Camera itself and the Target it focuses on. Both entail position properties. However, the pivotal detail lies in the rotation that the Camera takes concerning the target.
Perspective
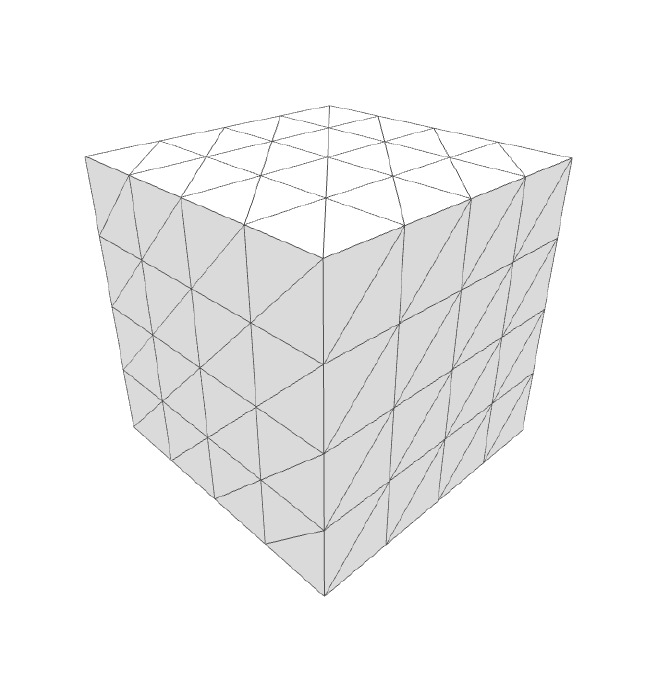
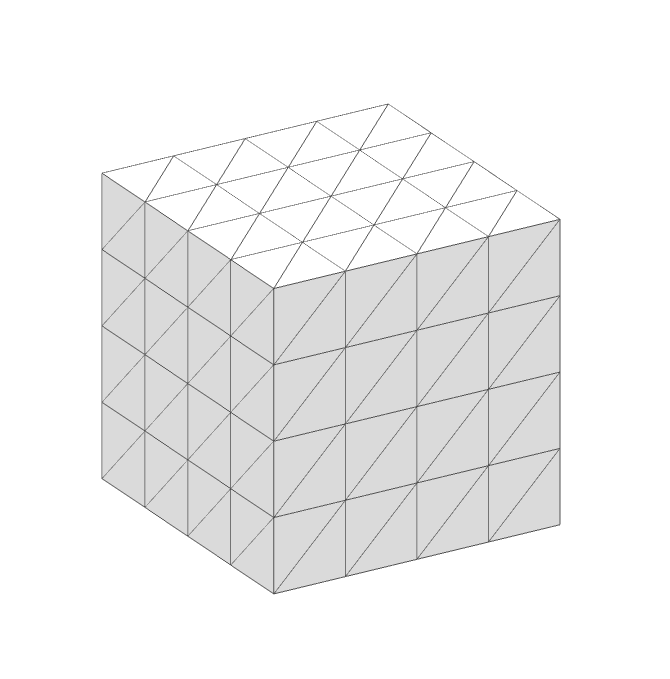
Orthographic
Focal Lenght
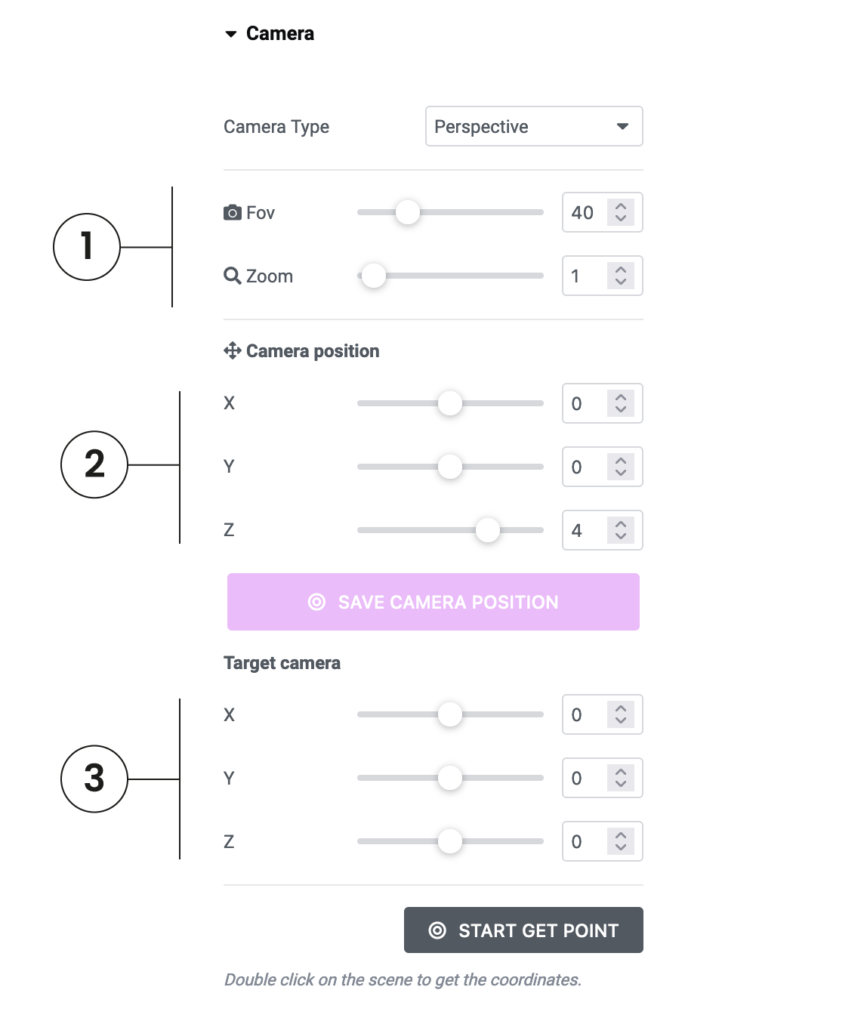
In all cameras, the focal length signifies the lens type, ranging from 10 to 200mm, with the default set at 40mm, mirroring human vision. The zoom feature also impacts viewing, where a setting of 1 equals the standard view.
Position
The camera’s position in the scene corresponds to the viewer’s perspective.
Target
The target is a point in the scene that represents where you’re focusing, essentially what you’re looking at.
SAVE position LIVE
The position parameters (X-Y-Z) for both the camera and the target can be controlled in real-time.
This means you can adjust your viewport framing – rotating, moving, and zooming, and then save these values as the default. This eliminates the need to move cumbersome “handles” in the editor, making the process quite convenient.
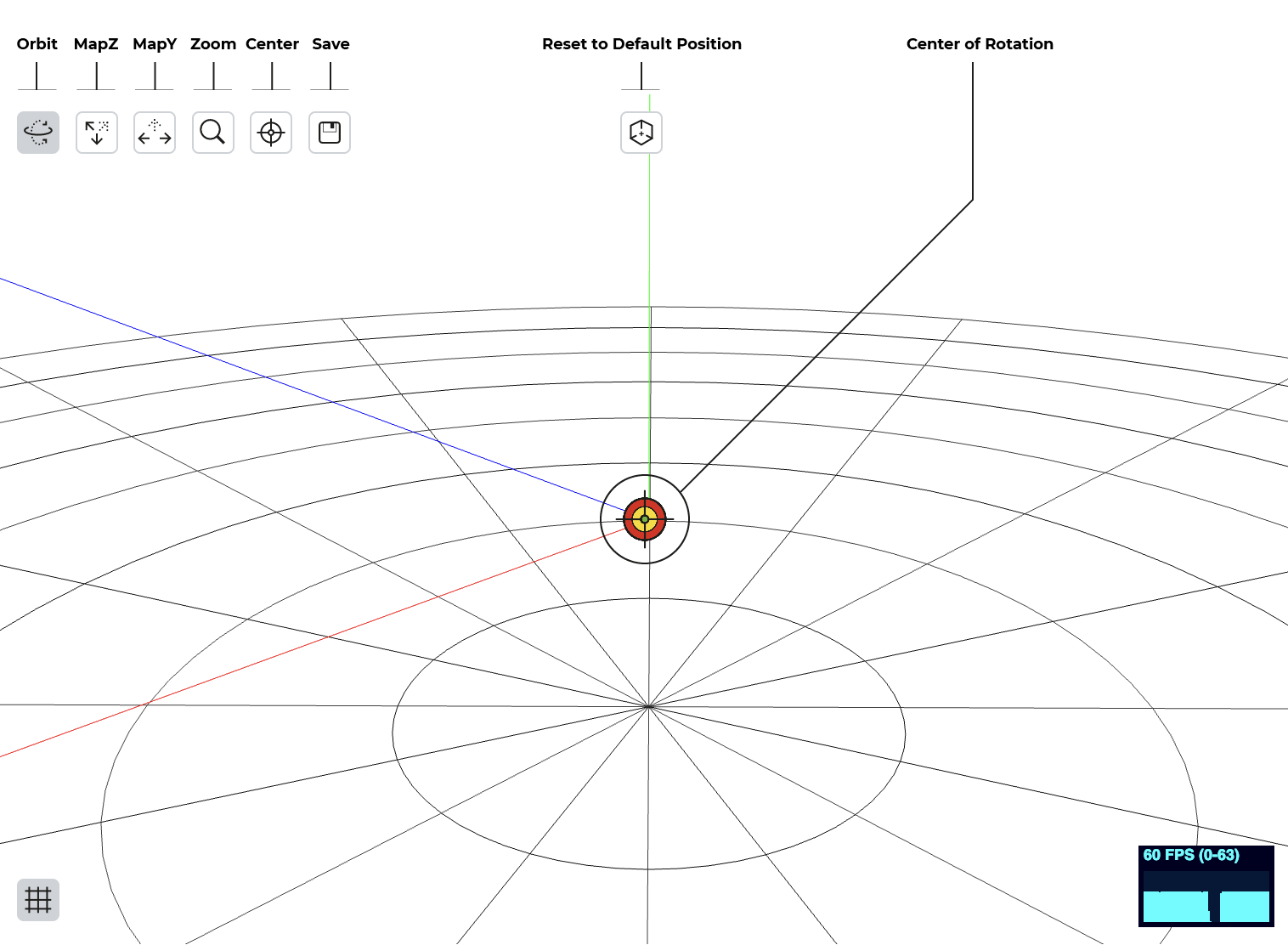
TOOLS Camera
These tools enable you to handle the live camera framing directly from the viewport within the editor.
Orbit
Rotating around the target
MapZ
Translating the X and Z map across the scene
MapY
Shifting the X and Y coordinates in the scene
Zoom
Zooming in and out in the scene is controlled by the mouse wheel
Center
By choosing an object, the scene’s target will center on it
Save
Once you’ve adjusted the scene to your liking, this button saves the values in the editor and sets them as the default.
Camera View
If you’ve moved the camera for better control of the elements while working on the scene, this button allows you to revert to the default view.
Viewpoints
For more precise control while modeling elements in scene development, you can shift the camera to a pre-determined viewpoint.
Center
This colored symbol shows the target’s position in the editor, around which the camera rotates.