Material Type
Depending on the simplicity of the reflectance and illumination models, performance can be improved. When choosing a material, keep in mind that MeshBasicMaterial and MeshLambertMaterial use fewer resources compared to MeshPhongMaterial, MeshStandardMaterial, or MeshPhysicalMaterial, but at the cost of lesser graphic accuracy.
Basic
This is a material used for simple geometry drawing (flat or wireframe).
This material is not influenced by lighting.
Lambert

This material is for non-shiny surfaces without specular reflections.
The material uses a Lambertian model, which isn’t based on physics, to calculate reflectance. This is suitable for simulating some surfaces like rough wood or stone, but it cannot replicate glossy surfaces with specular reflections, such as painted wood.

Phong
This material is for shiny surfaces with specular reflections.
The material uses a Blinn-Phong model, which isn’t based on physics, for calculating reflectance. This can effectively replicate shiny surfaces with specular reflections, such as painted wood.
Standard

This is a standard, physics-based material using the Metallic-Roughness workflow.
It allows you to create a material that reacts “correctly” under all lighting conditions, yielding a more precise and realistic result.
Note: To get the best results, always specify an environment map when using this material.

Physic

MeshPhysicalMaterial is an extension of MeshStandardMaterial, offering more sophisticated physics-based rendering properties:
- Physics-based transparency: ideal for thin, transparent surfaces like glass.
- Advanced Reflectivity: allows more flexible reflectivity for non-metallic materials.
- Sheen: suitable for depicting fabrics and textiles.
Note: Always specify an environment map when using this material for the best results.
Toon
This material is designed for toon shading.
Cel-shading or Cel-shader is a non-photorealistic method of rendering 3D models to make them hand-drawn. It uses bold black borders and a solid color palette to mimic a traditional cartoon style.
Normal
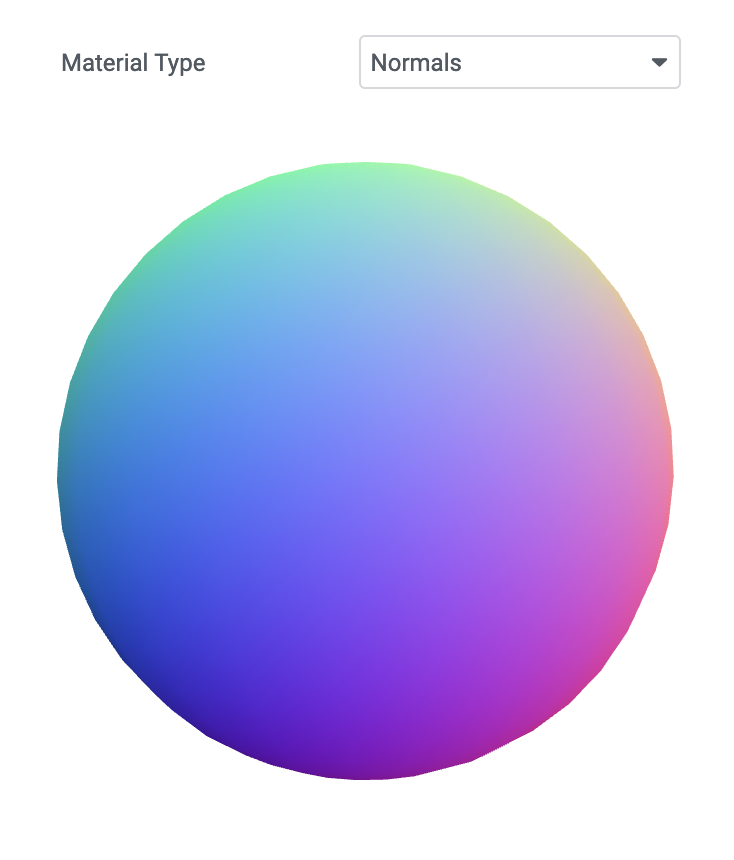
This is a material that converts normal vectors into RGB colors.
Wireframe Material
The wireframe model is a type of computer graphics representation used for 3D objects. In this method, only the edges of the object are drawn, leaving the object’s interior transparent (hence it looks like it’s made of “wire”). This method is simpler and considerably faster than solid surface representation as it requires less complex calculations.
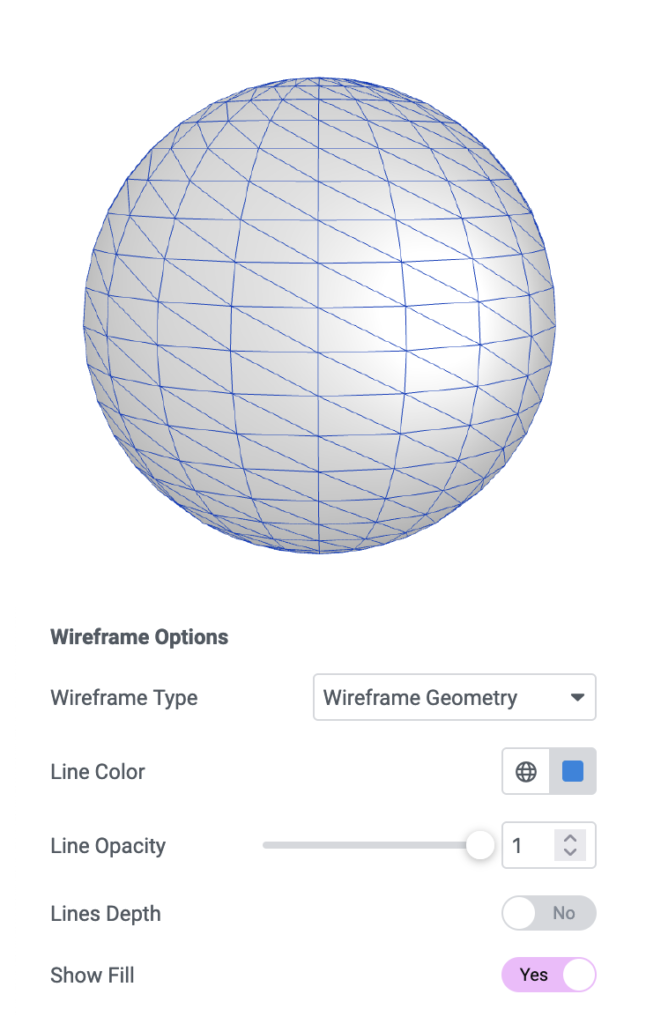
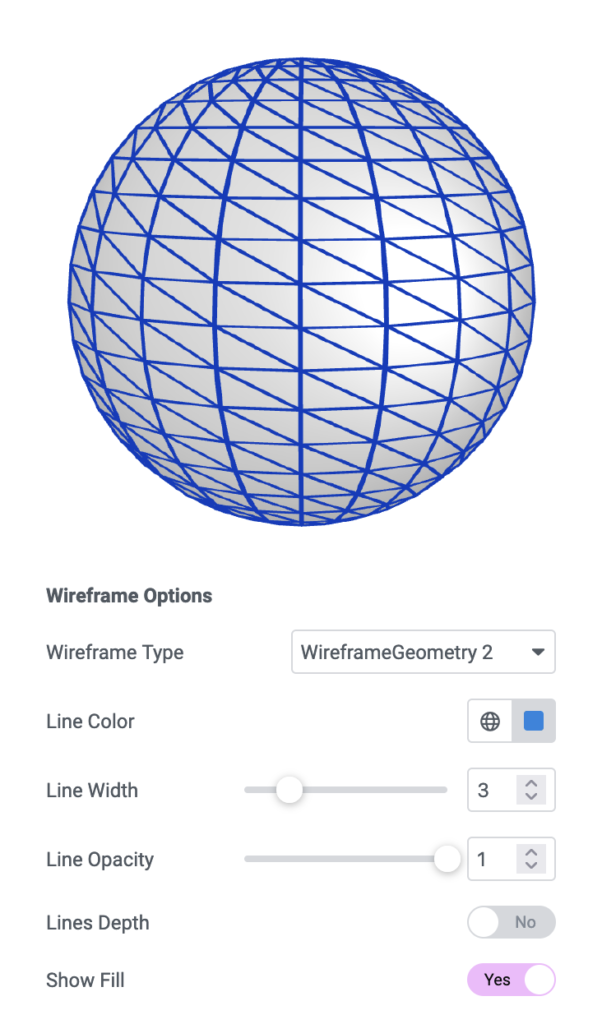
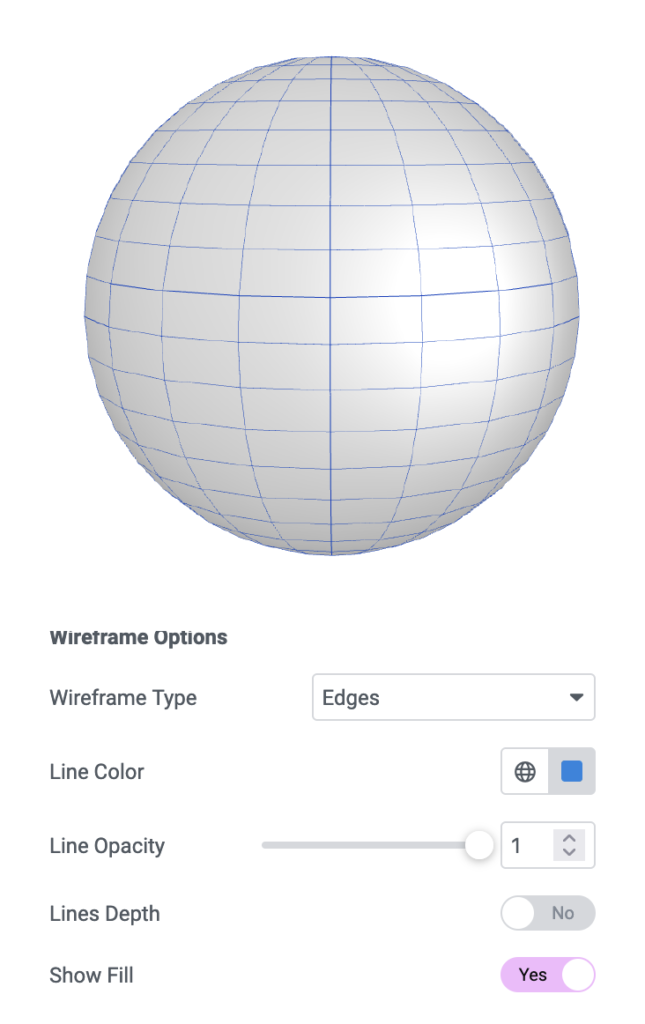
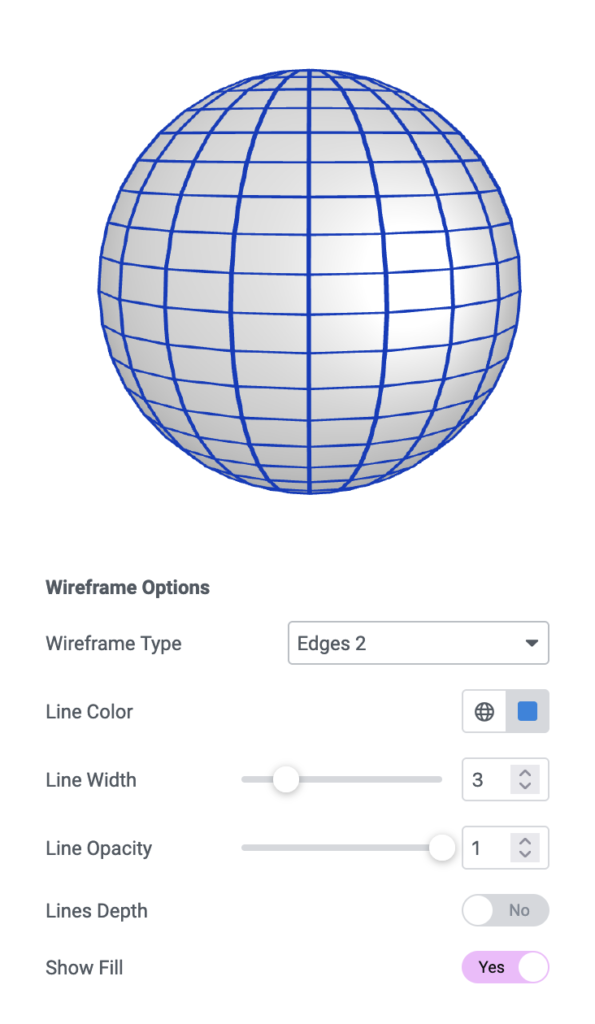
Wireframe
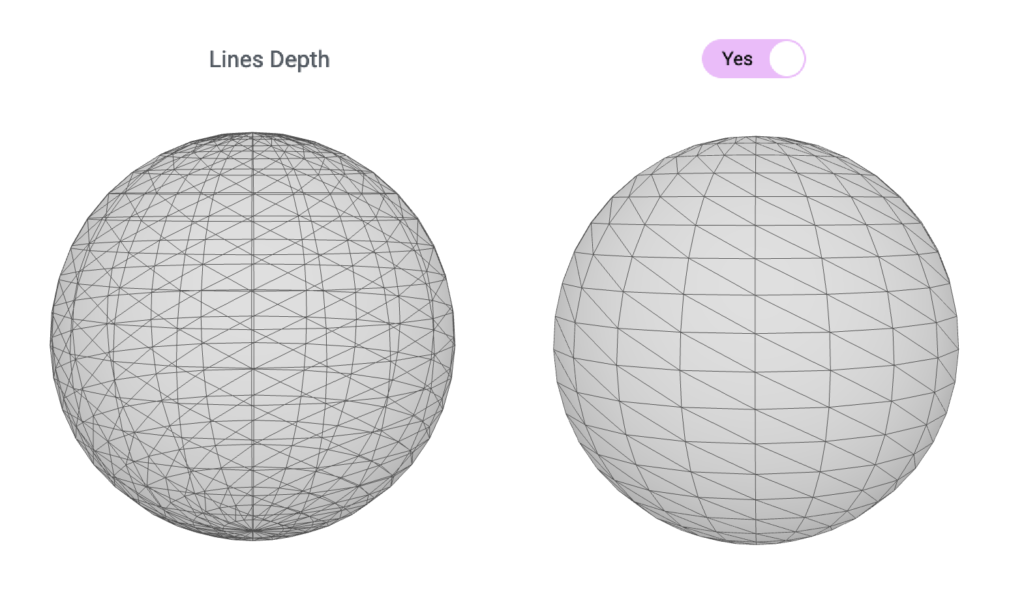
LineDepth
This feature prevents the lines behind the object from being drawn.
Wireframe
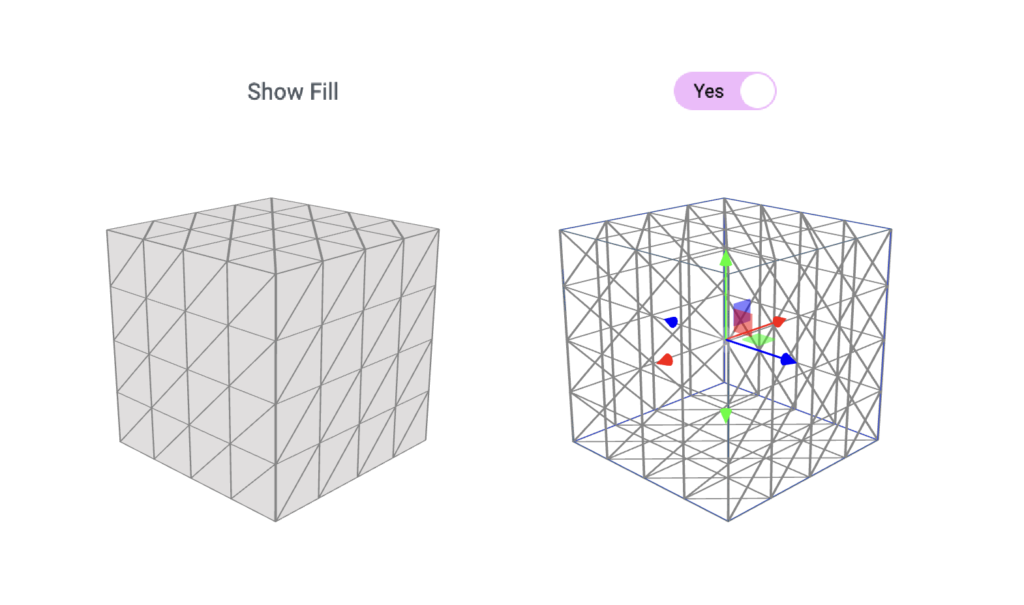
ShowFill
For a better visual appeal, we can consider a second element that serves as a filler within the “mesh”.
Material X
Material X is experimental and utilizes files in .mtlx format, which don’t have any parameters.
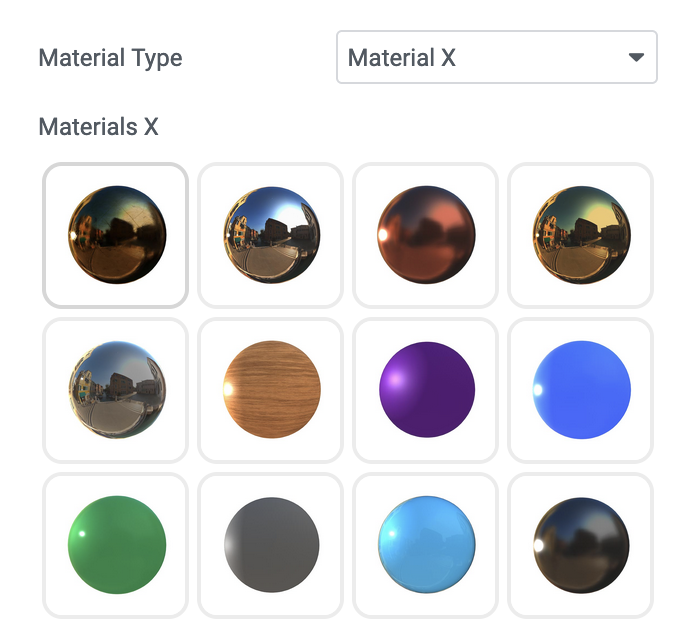

brasstiled

chrome

copper

gold

glass

wood

velvet

plastic

jade

grey
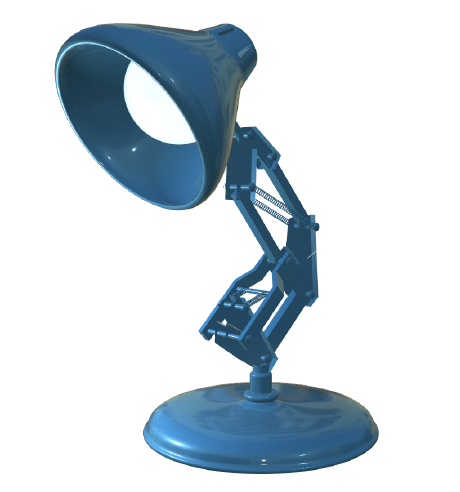

carpaint
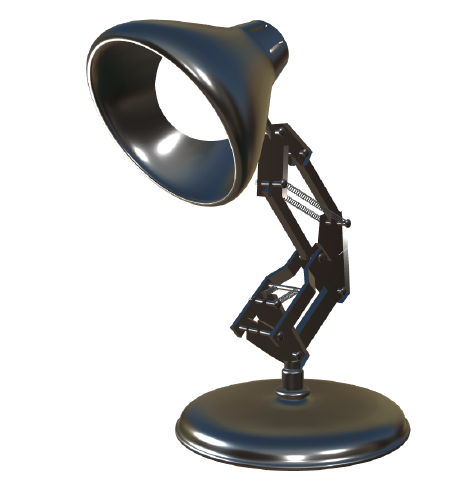

metalbrushed
Materials OPTIONS
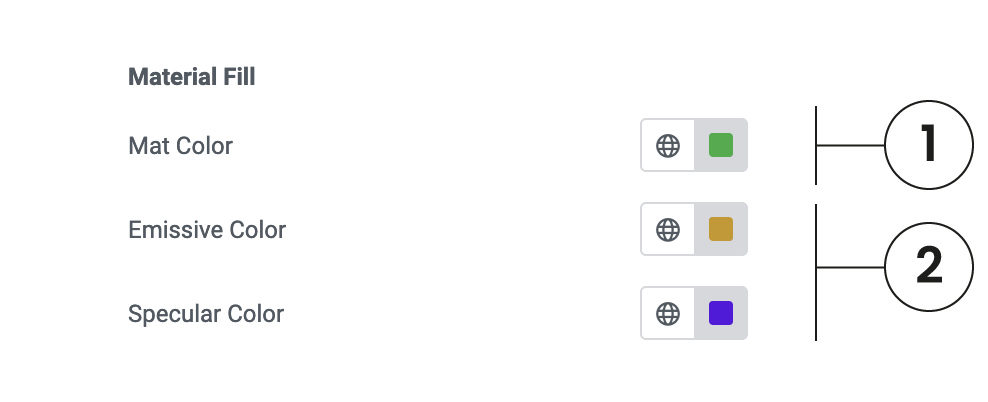

Color
For any material to be visible, it needs to be colored. With some advanced materials like “Standard” or “Physical”, we can also manage Emissive or Specular light.



Mode
Use Fog
This feature allows the Fog environment to have an effect when used.

Front
Back
Mode
Render Side
This setting allows for rendering of surfaces only from the
Front – Back – Double
Each option provides varying results.

Mode
Wireframing
This allows you to use any applied material in WireFrame mode.
This is different from using the WireFrame Material.

Mode
Flat Shading
This option presents the surface in a flat, non-rounded way.
Mode
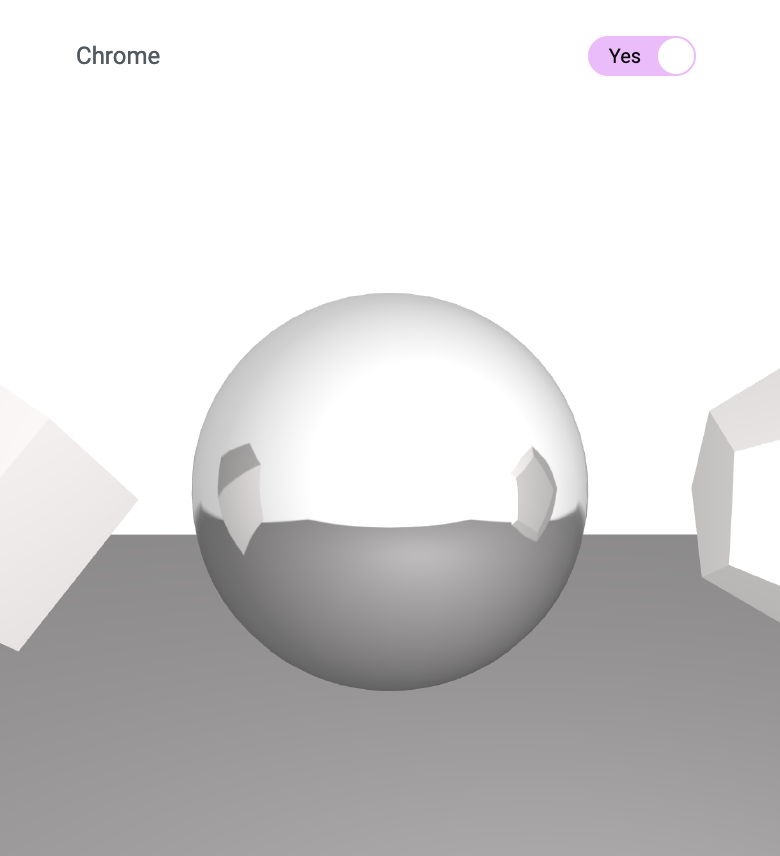
Chrome
The creation of the chrome reflection involves CubeCamera and cubeRenderTarget.
Image Maps
In computer graphics, texture mapping is a method allows one or more textures to be projected onto a 3D model’s surface using UV coordinates. It enhances the detail and realism of the model. Additionally, layering multiple textures can create special effects on 3D models, like light and fog.
Texture

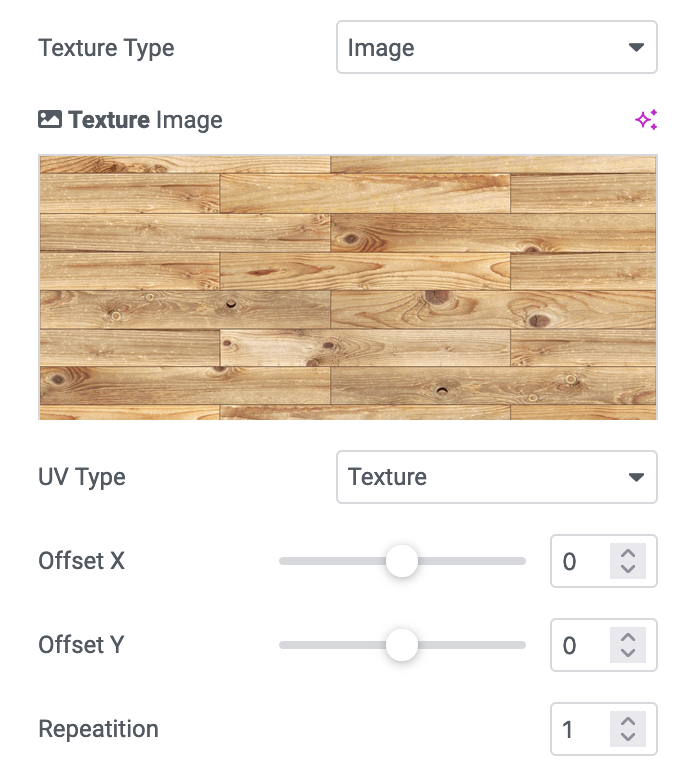
Emissive


Eviroinment

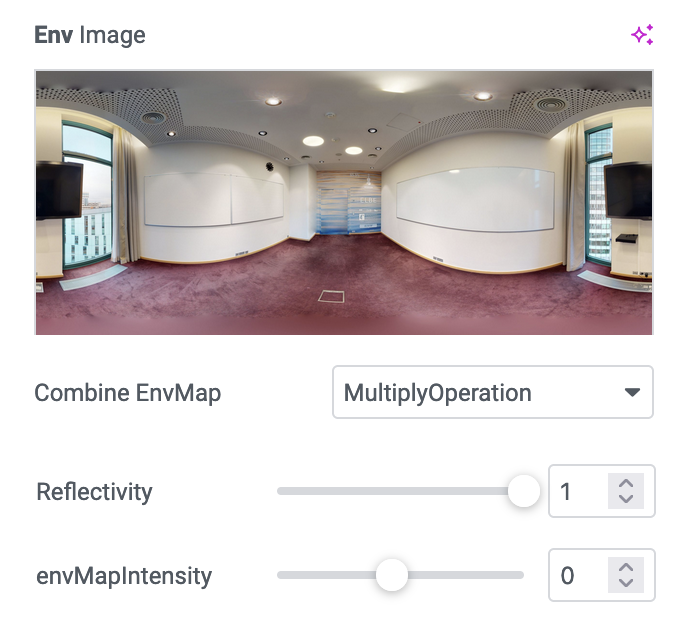
Bump


Metalness
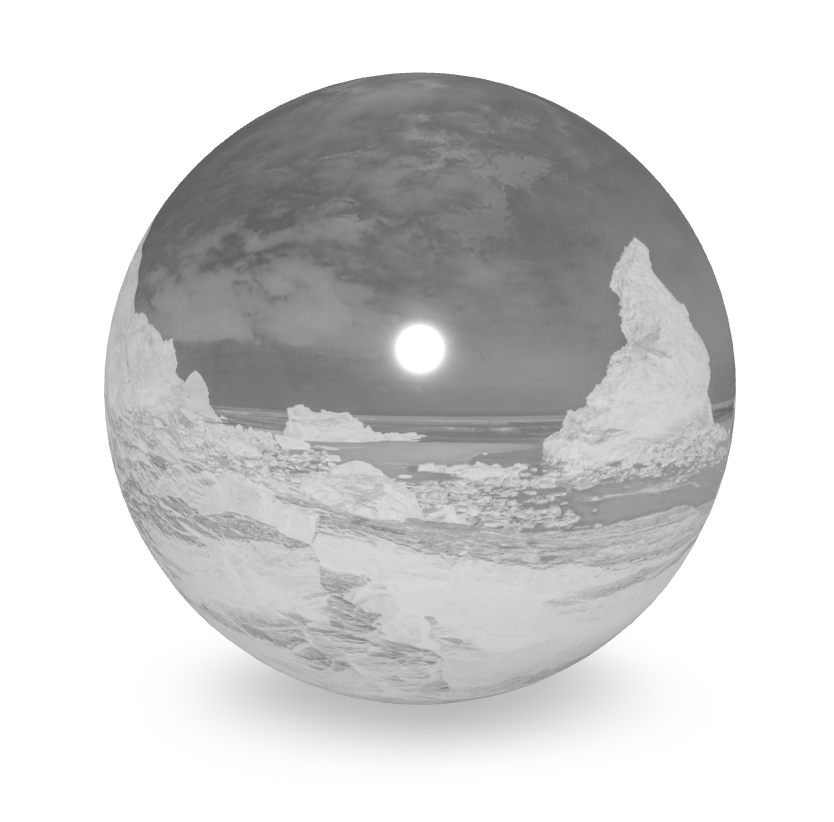

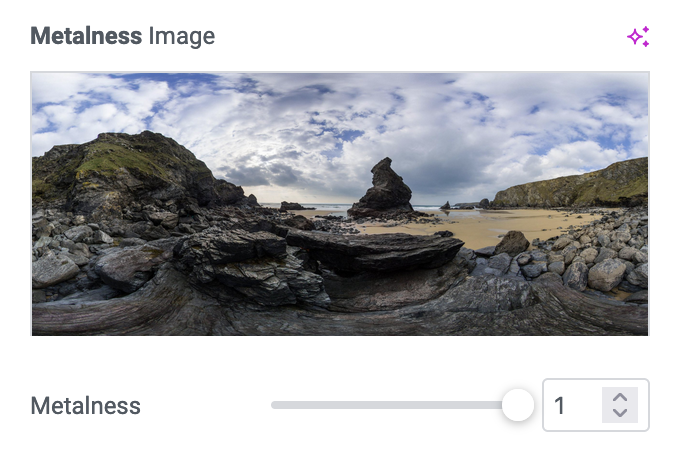
Roughness
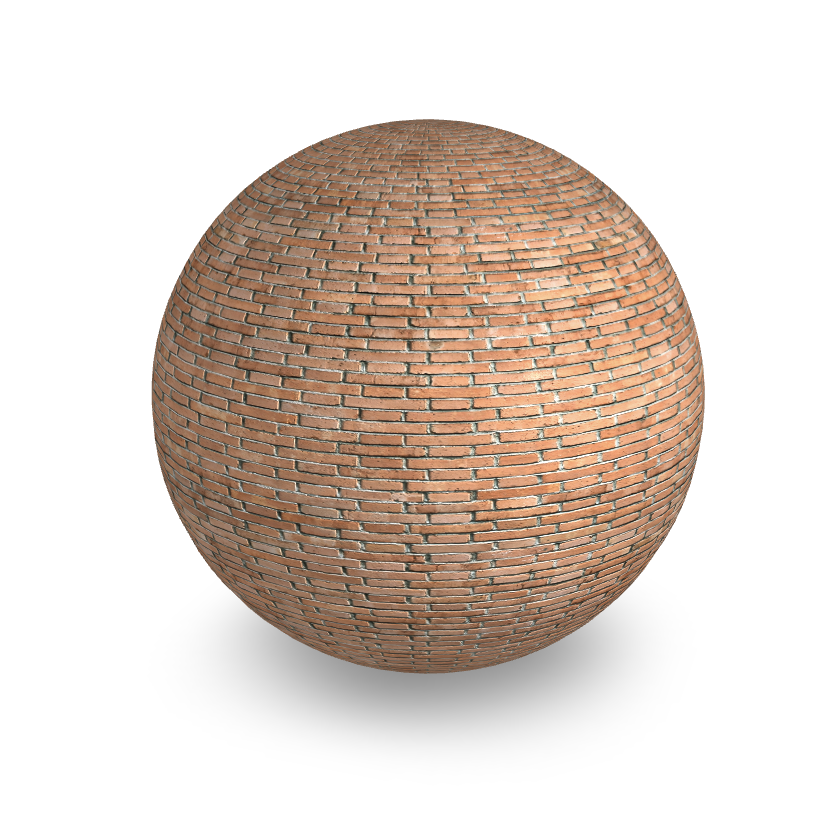


Normal
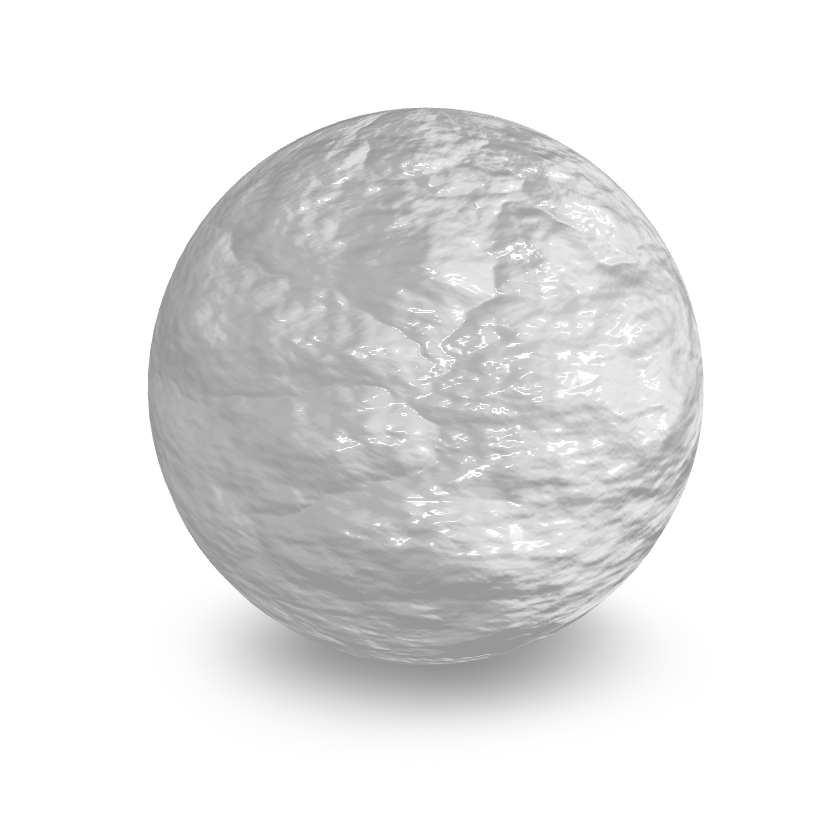


Displacement
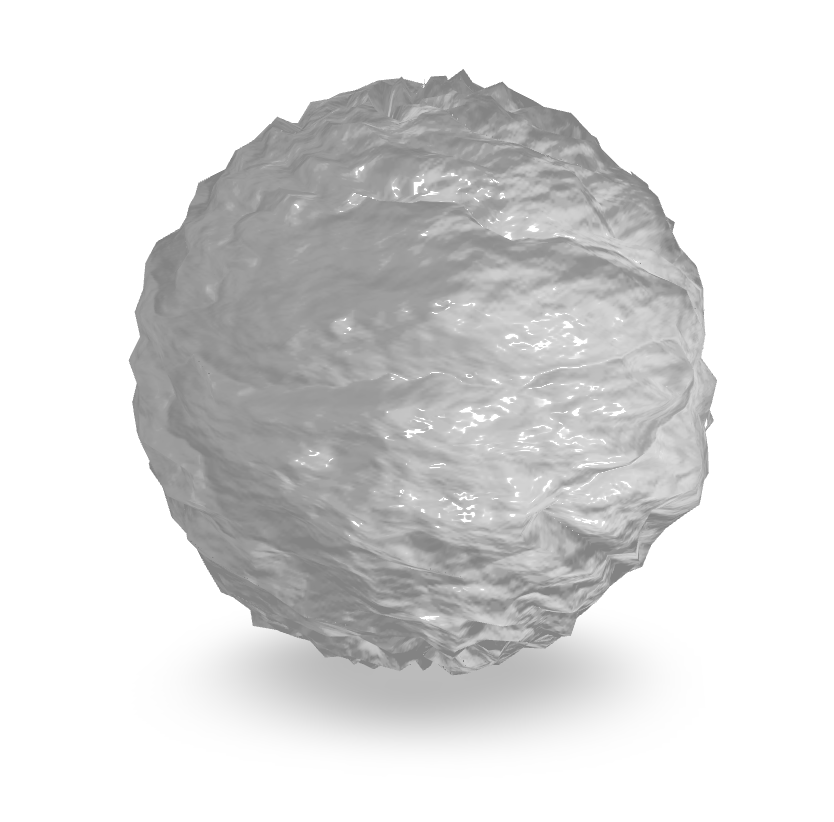


Transparent